- Your cart is currently empty.
How to Set Up an SSH Tunnel for MySQL Remote Access

SSH tunnelling or SSH forwarding is a method of transferring data over an encrypted SSH connection. SSH tunnels allow connections to local ports (on your computer) to be forwarded to a server (remote computer) over a secure channel.
For example, SSH forwarding is useful for transferring network data from services that use an unencrypted protocol (e.g. VNC or FTP), for accessing geo-restricted content, or for bypassing intermediate firewalls. In fact, the method allows any TCP port to be forwarded and traffic tunnelled over a secure SSH connection.
In the following, you will learn how to connect to a remote MySQL database on a local machine – by setting up an SSH tunnel. This is a more secure method than directly connecting your local machine to a remote MySQL database, as it establishes an encrypted SSH tunnel that forwards the port on your local machine to the remote MySQL server.
The procedure depends on the operating system you are running on your local machine.
Table of contents
Microsoft Windows
To set up an SSH tunnel on a Microsoft Windows computer, you need an SSH client. We recommend using PuTTY.
Once you have installed the program on your computer, follow these steps:
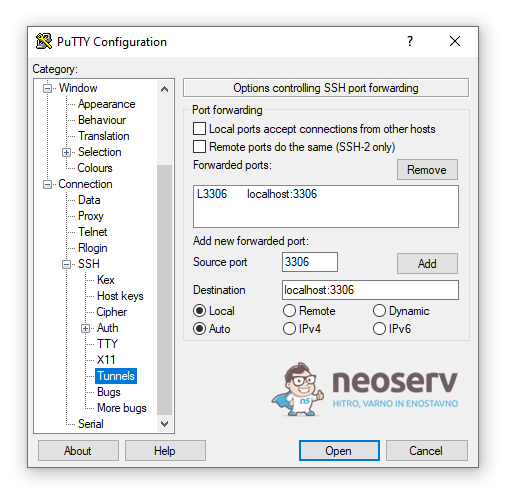
1. Open PuTTY, expand the Connection section, expand the SSH section within it and select Tunnels.
2. For the Source port setting, enter 3306 in the box and for the Destination setting, enter localhost:3306.
3. Make sure the Local and Auto radio buttons are enabled, then click Add.
4. Click on Session in the left menu to edit the basic PuTTY session settings.
5. In the Host Name (or IP address) field, enter your domain or IP address (e.g. vasadomena.si) and in the Port field, enter 5050.
6. Make sure the SSH radio button is enabled, then click Open.
7. If you see a security warning about the server’s host key, confirm by clicking Yes.
8. You will be prompted to loginas, first enter your username and then your password (use your login credentials to access the hosting package or cPanel).
9. When the remote server command prompt appears, the SSH tunnel is established. You can now use your MySQL client on your local machine.
To check that PuTTY is forwarding the port correctly, click on the icon in the top left corner of the PuTTY session window and check the Event Log. If the port forwarding is working correctly, it will say Local port 3306 forwarding to localhost:3306 or something similar.
Mac OS X/Linux
To set up an SSH tunnel on a computer running Mac OS X or Linux, follow these instructions:
1. Open a terminal and enter the command below at the command prompt, making sure to adjust the username (the username of the hosting package or cPanel account) and domain accordingly.
ssh -p 5050 uporabnisko_ime@vasadomena.si -L 3306:localhost:33062. Enter your password (the password of your hosting package or cPanel account) and press ENTER.
3. When the remote server command prompt appears, the SSH tunnel is established. You can now open the MySQL client that you are using on your local machine.
Troubleshooting
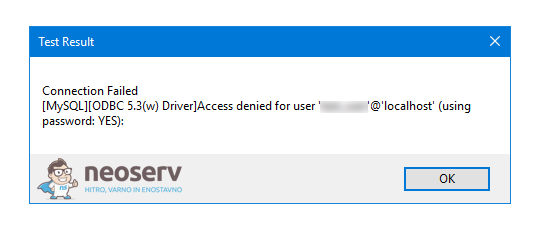
If you are developing on a local machine, the local copy of MySQL on port 3306 may already be running. In this case, you will encounter an error when establishing the connection.
To fix the problem, create a tunnel with other local ports and then connect to the remote MySQL server through these ports.
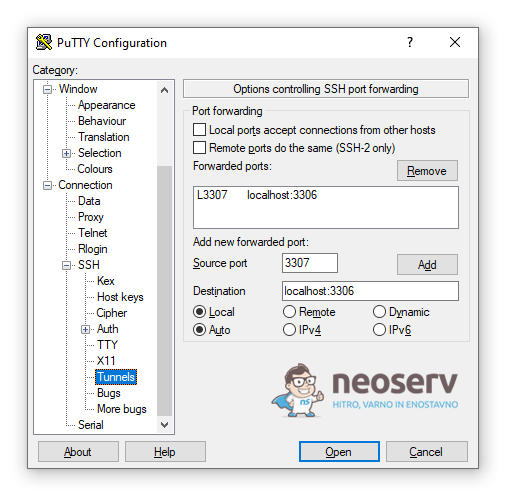
Microsoft Windows: If you are using PuTTY to create a tunnel, use an alternate Source port. For example, you can set port 3307.
Mac OS X / Linux: To set up a tunnel with local port 3307, use the following SSH command:
ssh -p 5050 uporabnisko_ime@vasadomena.si -L 3307:localhost:3306When using the above command, be careful to use your actual username (the username to connect to your hosting package or cPanel account) and domain.


COMMENT THE POST
Your comment has been successfully submitted
The comment will be visible on the page when our moderators approve it.