- Your cart is currently empty.
Why Email Attachment Is Larger Than the Original File
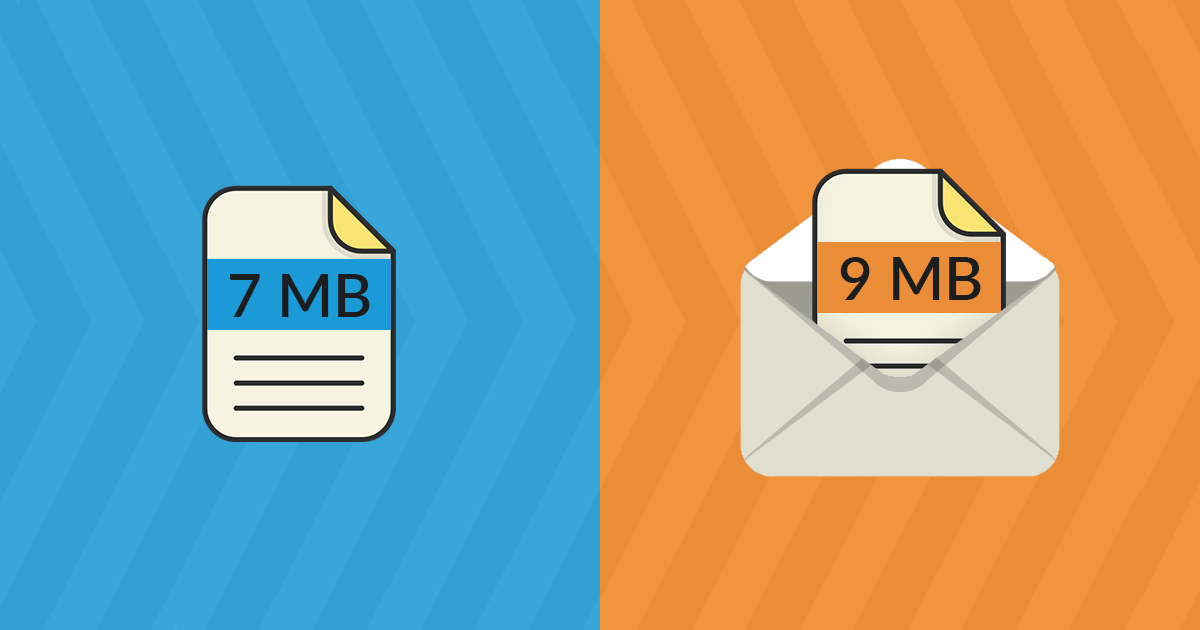
The technology that makes email possible is considered one of the oldest web technologies, which is why you may have been surprised when you attached a file (e.g. an image) to an email message and it suddenly took up more space than it did on your computer or mobile device.
What happened? Was something added to the attachment to make it larger than the original file? No, it’s plain writing – the file has been encoded into a simpler format that takes up more space. Some users even report a 45% increase in file size.
Interested in more? In the following, we will focus mainly on the difference between text and binary data, as this is the “culprit” for the difference in size between the original file and the attachment in the email message.
Text and binary data
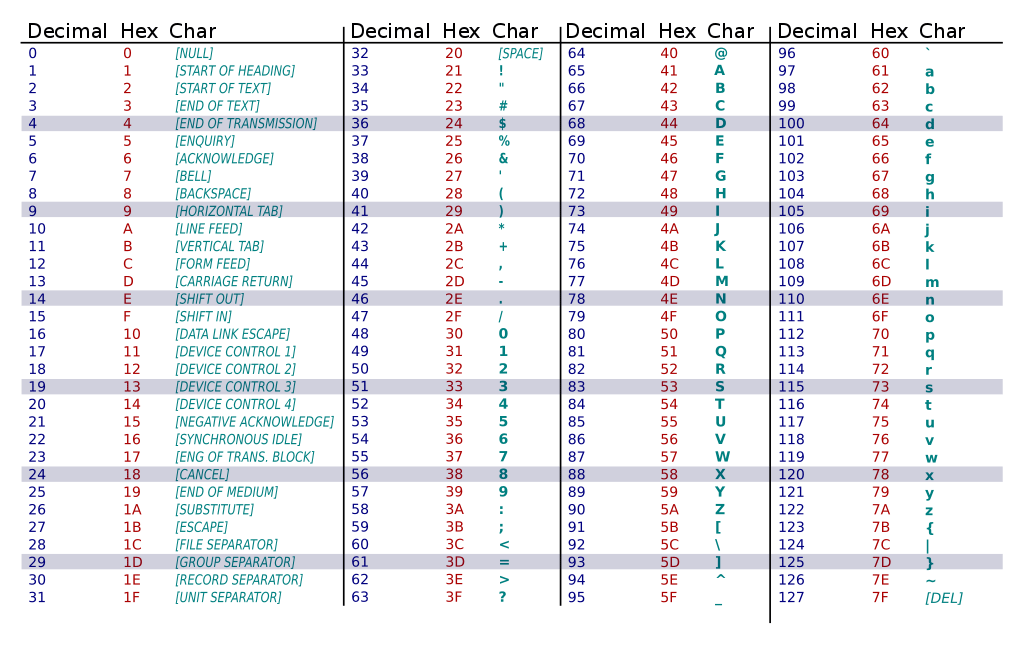
Textual data (letters, numbers and some symbols) are represented in the ASCII(American Standard Code for Information Interchange) standard by numbers from 0 to 127. For example, the capital letter A is represented by 65, the lowercase letter a by 97 and the # character by 35. 128 different characters exist according to this standard.
On the other hand, we have binary data represented by numbers from 0 to 255. You may already know that a byte also ranges from 0 to 255 and that all data on a computer is stored in bytes. Thus, the sizes of files, computer memories and hard disks are expressed in terms of bytes, whether they are kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes or terabytes.
Textual data stored on a computer can also be expressed in bytes, i.e. in values greater than 127. However, it is a characteristic of ‘ plain text’ data that it is written in values less than 128.
Why is this important?
E-mail messages originally contained only text. However, we all know that for a very long time email has also been used to send all kinds of attachments, such as images, PDFs, audio and video files, etc. And all such attachments are binary data.
This raises the question: How do you send data represented by values between 0 and 255 over a medium that only allows sending data consisting of values between 0 and 127? They need to be encoded. Binary data must be converted to text.
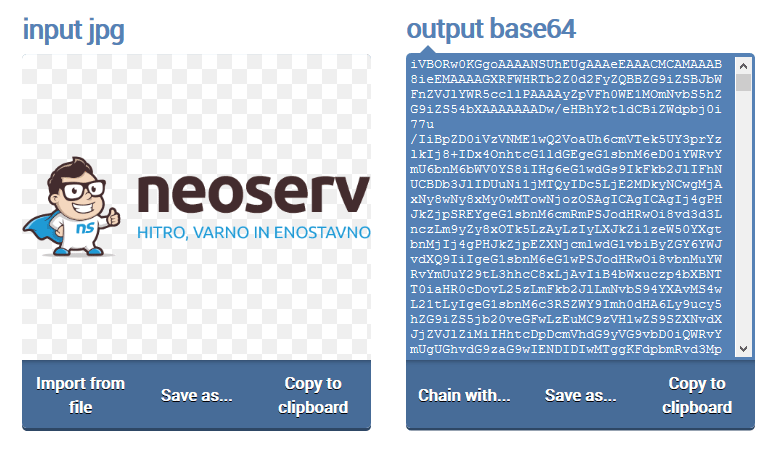
In the image above you can see what binary data encoded in text format looks like. The concrete example shows only the initial part of the base64 encoding of our logo in .PNG format.
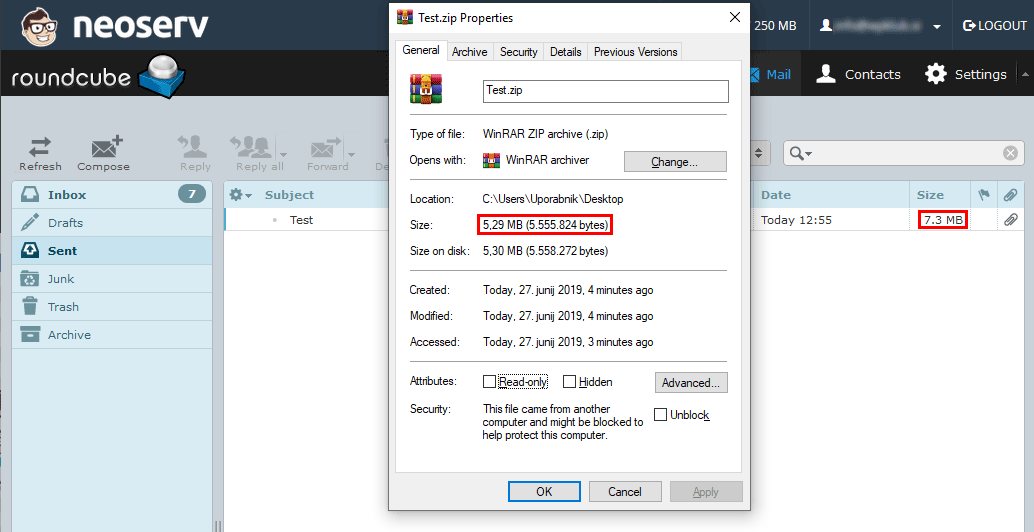
And what is the difference in file size before and after base64 encoding? As an example, we have taken a .ZIP file of NEOSERV promotional material, which takes up 5.3 MB of space, and 7.3 MB after encoding. This is a difference of 2 MB, which is 37.7% of the original file size.
Originally, only text data with values lower than 128 could be sent via e-mail. However, the need to send binary files soon became apparent. For this purpose, the mechanism presented above was used, which converts binary data into text data by means of encoding.
Although today most e-mail clients and e-mail servers allow the direct sending of binary files, this cannot be said for all of them. There are still systems and software that use basic encoding to transmit binary email attachments, which all email programs must support.
When an attachment takes up too much space …
So what does all this that we have written about today mean for the user? It means that the size limit of an email message (usually 25 MB) may vary from the size of the attachments the sender wants to send. So it’s possible that your attachments will need to take up less space than the maximum size of the email you send would otherwise allow.
In this case, you have two solutions:
- If you need to send a larger number of attachments, send them in smaller quantities (less recommended).
- If a single attachment is too large, use one of the dedicated applications for sending larger files (more recommended).

COMMENT THE POST
Your comment has been successfully submitted
The comment will be visible on the page when our moderators approve it.