- Your cart is currently empty.
Connecting to MySQL Database using Python

In today’s post, we’ll show you how to connect to a MySQL database using the Python programming language.
Python is one of the most widely used programming languages, its simple and elegant syntax makes it ideal for beginner programmers, while experienced programmers can enjoy the extensive list of available modules and features.
On the other hand, there is MySQL – a robust open source relational database management system based on the Structured Query Language (SQL). It is used in many applications and web servers.
Table of contents
Installing the module: mysql-connector-python
Before connecting to the MySQL database, you need to prepare a Python virtual environment and install the mysql-connector-python module.
1. Connect to your hosting package using SSH (instructions).
2. Create the virtual environment using the following two commands.
cd ~
virtualenv sqlenvThe virtualenv command creates a virtual environment named sqlenv. Subsequent commands in the procedure assume that the environment is named sqlenv. You can use any name you like for the virtual environment, but in this case remember to replace all sqlenv records with your own environment name.
If you are using an alternate version of Python (e.g. if you have manually configured a newer version of Python for your account), you can specify this version for the virtual environment. Example: to install the user-configured version of Python 3.8, use the following command:
virtualenv -p /home/username/bin/python3.8 sqlenvNote: replace the username in the above command with your actual username.
3. Enter the command below to activate the virtual environment.
source sqlenv/bin/activateThe command line now starts with a record (sqlenv) to indicate that you are working in a Python virtual environment. All subsequent commands assume that you are working in a virtual environment. If you log out of the SSH session (or disable the virtual environment with the deactivate command), make sure you reactivate the virtual environment before following the steps below.
4. Use the following command to update the taps in the virtual environment.
pip install -U pipThen install the mysql-connector-python package using the command below.
pip install mysql-connector-pythonSo, now you are ready to connect to the MySQL database using Python.
Connecting to the MySQL database
To connect to the MySQL database, use the code below. When doing so, make sure you record:
user_nameis replaced by the username of your database.- replace
the passwordwith the password of the database user. - replace
database_namewith the name of the database you want to connect to.
import axis
import sys
import mysql.connector
sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(__file__))
def application(environ, start_response) :
start_response('200 OK', [('Content-Type', 'text/plain')])
hostname = 'localhost'
username = 'username_name'
password = 'password'
database = 'database'
# Open database connection
MySQLconnection = mysql.connector.connect( host=hostname, user=username, passwd=password, db=database )
if MySQLconnection.is_connected():
# Prepare a cursor object using cursor() method
cursor = MySQLconnection.cursor()
# CREATE table Table with ID and Name attributes using execute() method
cursor.execute("CREATE TABLE `Table` (ID int NOT NULL, Name CHAR(20));")
# INSERT data in table Table
cursor.execute("INSERT INTO `Table` (`ID`, `Name`) VALUES ('1', 'NEOSERV'), ('2', 'Python'), ('3', 'App');")
else:
# ERROR message
message = 'Error connection to database!'
# Message of SUCCESS
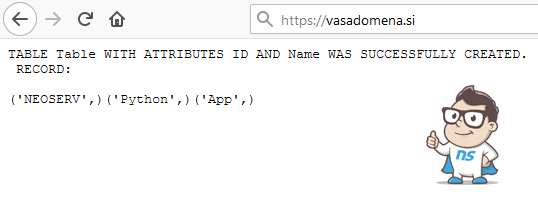
message = 'TABLE TABLE WITH ATTRIBUTES ID AND NAME WAS SUCCESSFULLY CREATED.\n RECORD:\n'
# SELECT data from table Table
cursor.execute("SELECT Name FROM `Table`;")
# SAVE data from SQL to variable
names = cursor.fetchall()
all_names = ''
for name in names:
all_names = all_names + str(name)
answer = '\n'.join([message,all_names])
# Close Cursor
cursor.close()
# Close database connection
MySQLconnection.close()
return [answer.encode()]Once you have a Connection object connected to the database, you can create a Cursor object. This allows you to use the execute() method to execute SQL statements.

COMMENT THE POST
Your comment has been successfully submitted
The comment will be visible on the page when our moderators approve it.